Introduction
In industrial applications, differences in motor efficiency can mean significant energy and financial costs.
Especially today, when energy prices are rising day by day, the use of low-efficiency IE1 motors not only increases the financial burden of enterprises, but also increases environmental pressure.
As global requirements for energy conservation and emission reduction increase, upgrading to higher-efficiency IE2, IE3 or IE4 motors has become the key to improving energy efficiency, reducing operating costs and achieving sustainable development.
This article will explore the differences between IE1, IE2, IE3 and IE4 low voltage 3 phase industrial AC motors to help you make a more informed motor selection decision.
What are IE classes?
IEC 60034 is a motor efficiency standard formulated by the International Electrotechnical Commission.
Its purpose is to standardize the energy efficiency of motors and prevent energy waste and environmental pollution caused by the use of inefficient motors.
This standard sets the energy efficiency standard for motors as
IE1: standard efficiency
IE2: high efficiency
IE3: Advanced Efficiency
IE4: Super Premium Efficiency
IE5: (no specific name defined)
Five levels (originally four levels), the later ones are more efficient. IE5 is currently the highest efficiency level. IEC 60034 is not only applicable to the international market, but has also become a mandatory standard in many countries and region.
What is IE1 motors?
Define and describe the characteristics of IE1 motors.
IE1 motors are standard efficiency motors and belong to the International Energy Efficiency (IE) class.
IE1 motors are considered the 1st generation of energy-efficient motors and are typically used in applications where energy costs are not a major consideration.
They are less energy efficient than other IE motors and are often older designs.
The applications and limitations.
IE1 motors or standard efficiency motors are typically used in applications where energy costs are not a major consideration.
It is commonly used in petroleum, chemical, metallurgy, cement, paper making and other industries, and can be used in conjunction with pumps, fans, compressors and general machinery.
IE1 motors are also used on older machinery or in areas where energy efficiency regulations are less stringent.
As of July 2023, new European Ecodesign rules will no longer allow new electric motors with powers between 0.75 kW and 1,000 kW to achieve the IE1 and IE2 efficiency classes.
The new rules also require motors with power between 0.12 kW and 0.75 kW to have an efficiency class of IE2+Drive or higher, and motors with power between 75 kW and 200 kW to have an efficiency class of at least IE4.
What is IE2 motors?
Define and describe the characteristics of IE2 motors.
IE2 motors are high-efficiency motors that are part of the International Energy Efficiency (IE) standard.
They have an output range of 0.75kW to 355kW, a speed range of 1000-3600rpm, and an RPM frequency of 50Hz or 60Hz.
IE2 motors are also limited to 2, 4 and 6 poles, with aluminum frame sizes 80–160.
Main usage scenarios and benefits.
IE2 motors are high-efficiency motors that can be used in a variety of applications, including:
Machinery: machine tools, woodworking machinery, textile machinery, packaging and labeling machinery, conveyor belts, construction machinery
Transport: Compressor Transport Machinery
petroleum : petroleum
Chemical industry,
Mining and other places with harsh environments
Marine: In marine applications,
IE2 motors are known for their high efficiency, low noise, compact structure and easy maintenance.
They also have high protection levels and high insulation levels.
IE2 motors have IP54 protection standards, which means they are completely protected against dust and water splashing from all directions at a flow rate of 10 liters per minute for five minutes.H3:Define and describe the characteristics of IE3 motors.
What is IE3 motors?
Define and describe the characteristics of IE3 motors.
The IE3 motor is a high-efficiency motor that meets the latest European electrical efficiency standards.
IE3 motors are often mandated by national regulations due to their energy-saving capabilities. IE3 motors offer several advantages, including:
High efficiency: Compared with standard motors, IE3 motors reduce motor losses by 30-40%.
Long motor life: IE3 motors have twice the coil insulation life of standard motors.
Variable frequency operation: IE3 motor can operate at 1:10 or 1:20 constant torque.
Low noise and vibration: IE3 motors have advanced technology to reduce noise and vibration.
Reasons for being the standard choice in many countries.
Efficiency: IE3 motors have 30-40% lower motor losses than standard motors.
Energy Saving: IE3 motors are more efficient than IE2 motors, helping to reduce operating costs and increase profitability.
Longer service life: IE3 motors have twice the coil insulation life and 2.5 times the bearing life of standard motors.
Lower operating temperature: IE3 motors operate at lower temperatures, reducing thermal stress on the motor, bearings and terminals, and extending the service life of the motor.
Noise and Vibration: IE3 motors use advanced technology to reduce noise and vibration.
Flow and Pressure Control: IE3 motors feature optimized design parameters for improved flow and pressure control.
Protection: The IE3 motor has IP55 protection against dust and water jets from a distance of 3 meters at 12 LPM for 3 minutes.
Examples in practical applications.
Machine tools,
air compressors,
pumps,
fans,
reducers,
conveyor belts,
mining machinery,
metallurgical equipment,
airport escalators,
hospital HVAC systems
What is IE4 motors?
Define and describe the characteristics of IE4 motors.
IE4 motors are motors designed for high energy efficiency, the abbreviation IE4 stands for “Extra Efficient”.
They are the latest generation of electric motors designed for applications where the motor operates almost continuously and where high energy costs require the highest possible efficiency.
IE4 motors are asynchronous, low-voltage, three-phase TEFC motors that significantly reduce energy costs through low-energy operation.
Applications in ultra-high efficiency requirements.
The IE4 motor is an electric motor used in a variety of industries, including
HVAC systems,
food,
air handling,
extraction.
pumps,
fans
compressors.
Analysis of long-term return on investment.
IE4 motors save investment thanks to their energy efficiency, durability and low maintenance requirements.
IE4 motors are 30% more efficient than conventional motors, meaning they use less energy to achieve the same level of performance.
This means significant energy savings, reduced operating costs and a lower carbon footprint.
Energy Saving: IE4 high-efficiency motors are designed to be efficient, which means they consume less energy for the same workload.
This means significant energy savings, reduced operating costs and a lower carbon footprint.
Longer service life: IE4 motors have a longer service life compared to other types of motors, mainly due to their high efficiency levels. This means lower maintenance costs and higher productivity.
Compliance: IE4 motors comply with the latest energy efficiency regulations, making them ideal for companies looking to meet sustainability goals.
Reliable: IE4 motors are designed to handle complex operation and frequent start-stop cycles, making them a reliable choice for demanding applications.
What are the differences between IE1 and IE2 motors?
(1) The number of poles of IE1 motor is 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12. The IE1 motor has a speed range of 500rpm to 3600rpm. The number of poles of the IE2 motor is 2, 4, and 6. IE2 motors have a speed range of 1000rpm to 3600rpm.
(2) The aluminum shell size of IE1 motor is 56-200. The aluminum frame size of IE2 motor is 80-160.
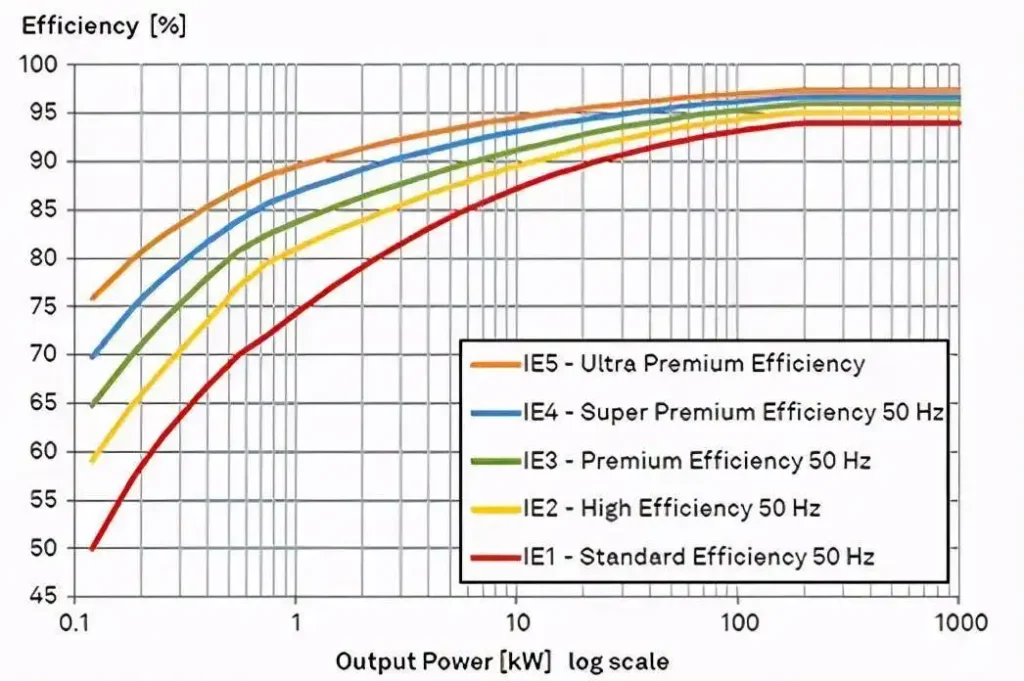
(3) High efficiency, IE2 is 3% higher on average than IE1.
(4) More high-quality materials need to be used. The cost of IE2 motor is 25%~30% higher than that of IE1.
(5) Due to the lower operating temperature, the motor has a longer life and can reduce maintenance costs.
(6) The starting current is larger under typical design conditions.
(7) The rotor inertia is large.
(8) The speed is higher under rated load and the slip is smaller.
What are the differences between IE2 & IE3 motors?
1.The number of poles of IE2 motor is 2, 4, and 6. The number of poles of IE3 motors is 2, 4, 6, and 8.
2. The speed range of IE2 motor is 1000rpm to 3600rpm. The speed range of the IE3 motor is 750rpm to 3600rpm.
3. IE 2 motors are approximately 92-3% efficient, while IE3 motors are approximately 93.6% efficient. These motors can run continuously on warehouse conveyors for up to 3,500 hours a year. In this case, the more efficient IE3 motor will save approximately 1580 kWh of energy throughout the year.
4. In addition, many countries now have regulations requiring the use of IE3 motors in certain applications. For example, the European Union mandated the use of IE3 motors for motors with rated power of 7.5kW and above in 2017.
5. The benefits of upgrading to an IE3 motor don’t end there. They also last longer, which means fewer replacements and less downtime. They also run cooler than IE2 motors, which reduces maintenance costs.
6. IE3 motors generally comply with more stringent energy efficiency regulations than IE2 motors. For example, IE3 motors can meet the requirements of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60034-30 standard, which specifies the efficiency levels of rotating electrical machines.
7.The cooling technology of IE2 motor is IC411. The cooling technologies for IE3 motors are IC411 and IC416.
What are the differences between IE3 and IE4 motors?
1.The aluminum frame size of IE3 motor is 80-160. The aluminum frame size of IE4 motor is 100-160
2.The cast iron frame size of IE3 motor is 80-400. The cast iron frame size of IE4 motor is 100-315.
3. IE4 motors are more efficient than IE3 motors. The efficiency of IE4 motors is about 97%, while the efficiency of IE3 motors is 96%. IE4 motors are also known as “ultra efficient” motors, while IE3 motors are known as “ultra efficient” motors. IE4 motors are more efficient because they use higher quality materials and improved rotor and stator designs
4. Both motors use IC411 and IC416 cooling technology.
5. IE3 motors are available in aluminum frame sizes 80-160 and cast iron frame sizes 80-400, while IE4 aluminum frame sizes are 100-160 and cast iron frame sizes 100-315.
6.IE4 motors are generally more expensive than IE3 motors due to their higher efficiency and more advanced design.
7. IE4 motors comply with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) high-efficiency motor standards, and IE3 motors comply with the high-efficiency motor standards. This means that IE4 motors must meet more stringent efficiency requirements.
Motor Selection Guide
When it comes to electric motors, there are many types to choose from.
There are many different types of applications using electric motors, each with its own unique requirements.
Considering the range of applications and motor types available, selecting the right motor for a specific application can be a complex task.
In this article, we’ll discuss six key factors you should consider when selecting an electric motor for your project.
Performance requirements:
The first step in selecting an electric motor is to determine the performance requirements of the application (power, torque, speed, and acceleration requirements).
*In order to determine power requirements, information is needed about the amount of work to be done and the time frame within which it needs to be done.
Then the required power can be calculated using the following formula:
Power (W) = (Force x Distance)/Time.
*In order to calculate torque requirements, you must obtain data on the magnitude of the force that needs to be applied and the distance from the center of rotation where the force is applied.
Then you can use the following formula:
Torque (Nm) = force (N) x distance from center of rotation (m).
*To determine speed requirements, you need to know how fast the object or load needs to rotate.
This information can be used to calculate the required speed. Speed requirements can be calculated using the following formula:
Speed (RPM) = (60 x speed (m/s)) / (2 x π x radius (m)).
*If you need to accelerate an object to a specific speed within a specific time, you must know the starting speed, final speed, and acceleration duration. Then you can use the following formula:
Acceleration (m/s^2) = (final velocity (m/s) – initial velocity (m/s)) / time (s).
Once you determine the power, torque, speed, and acceleration requirements of your application, you can use the motor manufacturer’s data sheet to select the correct motor that meets these requirements.
Dimensions and installation:
When selecting a motor, it is critical to consider the physical space available to the motor as well as any weight or vibration limitations.
Electric motors come in a variety of sizes and mounting options, from compact designs to larger, heavier models.
It is crucial to choose a motor that fits the available space and meets any weight or vibration requirements.
Environmental conditions:
The operating environment of a motor has a significant impact on its performance and service life.
For example, motors used in harsh or corrosive environments may require special coatings or materials to prevent damage.
Likewise, motors used in high-temperature environments may require additional cooling mechanisms.
Efficiency
The efficiency of electric motors varies widely, which can have a significant impact on operating costs and environmental impact.
To meet the required standards for motor efficiency, engineers can take a number of measures. There are several steps they can take:
*Choose motors with high efficiency ratings: These motors are designed to meet specific efficiency requirements and can save energy and reduce operating costs over time.
*Consider load factor: When selecting a motor, it is important to consider load factor, which is the percentage of rated motor power required by the application.
Motors that are too large or undersized for the application can result in reduced efficiency and increased energy costs.
*Correct installation and maintenance: Correct installation and maintenance of motors can also play a role in ensuring high efficiency.
This includes things like ensuring belts are properly aligned and tensioned, as well as regularly inspecting and replacing worn or damaged parts.
Cost
You need to consider the cost of the motor and how it fits into your budget.
While it may be tempting to choose the cheapest motor available, remember that higher quality motors offer better performance and longer life, which can ultimately save you money in the long run.
Also, consider any ongoing maintenance or repair costs associated with your motor.
Future Trends and Developments
Anticipating new standards (e.g., IE5) that might emerge in the future.
There is an increasing focus on the efficiency of electric motors to reduce energy consumption and help us meet carbon emissions targets around the world.
Considering that 45% of electricity is converted into motion through electric motors, these changes could be significant in halting climate change.
Electric motors play an important role in our daily lives, with an estimated 300 million motor-driven systems operating every day, from simple hair dryers to refrigerators to industrial manufacturing machines.
Electricity generation produces large amounts of carbon dioxide emissions, which contribute to global warming; therefore, in order to reduce emissions and help the environment, improving motor efficiency is one of the best places to start.
The energy efficiency of electric motors is expressed in International Energy Efficiency Classes (IE), with IE1 being the lowest class and IE5 being the highest class.
The super-advanced efficiency class IE5 defined by the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) goes well beyond the new minimum standard IE3 for the IE class of low-voltage motors set and implemented by the EU Ecodesign Regulation in July 2021.
Advantages of IE5 motors
Energy losses are reduced by up to 40% compared to IE3 induction motors and 50% compared to IE2 motors.
Reduce CO2 emissions
The perfect solution for motor retrofits, easily retrofitted into existing installations or incorporated into new projects and OEM designs
Improve reliability and reduce maintenance costs
Reducing heat generation/lower operating temperatures protects the motor and extends its service life.
Not only can IE5 motors have a clear positive impact on the environment compared to their less efficient counterparts (IE1-4), end users can also benefit from reduced energy use and expenditure as well as a longer service life and less waste from the motor itself.
Benefit from frequent needs. maintain.
Depending on its power and usage, a more efficient motor can save hundreds to tens of thousands of pounds over its lifetime.
This is especially true for motors that run continuously or for long periods of time and for larger motors that produce greater savings.
Conclusion
Ready to enhance your operational efficiency and reduce energy costs?
Upgrading to higher efficiency motors like IE2, IE3, or IE4 is not just a choice—it’s an investment in your future.
Don’t let outdated technology hold back your business.
Contact LUPMOTORS today to discuss how our energy-efficient motor solutions can benefit your specific applications and help you achieve your sustainability goals.
Make the switch now and start seeing the savings and benefits of improved motor efficiency!